We provide a full lineup of human-friendly medical devices.
Extracorporeal circulation (artificial heart-lung) is a medical procedure in which blood is taken from a patient’s circulation for gas exchange and returned to the circulation as an alternative to the heart and lungs. This procedure is required when the heart must be temporarily stopped during cardiac surgery. The “Heart-lung machine” for extracorporeal circulation plays a role as an “alternative system for vital functions” and a “life-support system” that can adapt the following biological functions:
(1) Pump function of the heart (blood pump)
(2) Role in the gas exchange function of the lungs (oxygenator)
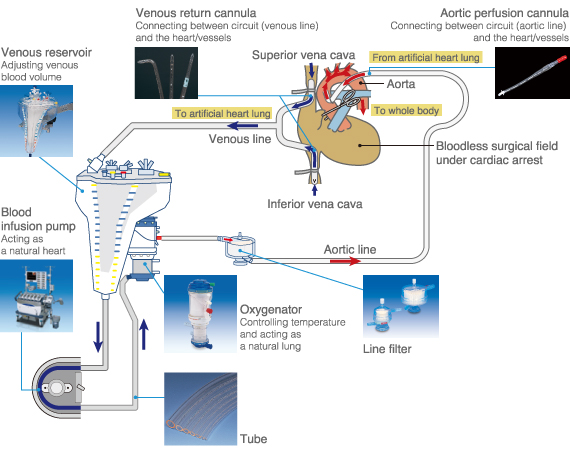
As described in the above figure, an incision is made into the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. Flexible tubes are separately inserted into each vena cava.
The venous blood is dropped or pumped through the plastic tube. Next, oxygen is added to the blood with the oxygenator. Then the blood is sent back to the aorta with the blood infusion pump through the aorta cannula. Finally, the oxygenated blood flows back by the aforementioned method.
The electrosurgical unit is one of the most commonly used medical devices in surgery. The electrosurgical unit produces Joule heat by generating electric current to a local area on the body with a high-frequency current. This heat can coagulate a bleeding site or make an incision in the tissue in the body. In addition, surgical operation can be continued by suppressing bleeding. The surgeon, therefore, performs smoothly and decreases the risk to the patient.

There is a concern whether the patient will be shocked when receiving electricity on the living body. In fact, the electricity used in this device is a high-frequency current. This high-frequency current has the characteristic that it does not pass electrical stimulation to the nerves and muscle. Therefore, it can be safely used in patients without electric shock (irritation).
The high-frequency current of the electrosurgical generator travels into the body through the tip of the electrode. To collect the electric current to the generator, one electrode of “palm size” called a “patient return electrode” will be attached. Please imagine the following: this patient return electrode is an expanded version of a gel electrode used for an electrocardiogram.
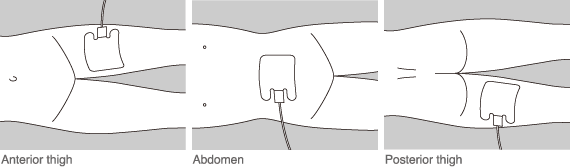
The part to which the patient return electrode is attached varies according to the maneuver of the surgery. It may commonly be attached to a “part with good muscle tone with blood circulation.” The main portions include femoral parts, hips, the abdomen, and the upper arm.
For patients with hair on the part where the electrode is attached, removing (shaving) the hair may be necessary. This is to allow as much of the high-frequency current to be collected by the electrode as possible. By raising the coherency between the skin and the electrode, the current can be collected more efficiently.
The unit consists of only three instruments, the “main body (generator),” the “tip electrode” and the “patient return electrode.”
For a tip electrode generating high-frequency current in the living body, a variety of shapes and lengths are available according to various applications (electrodes suitable for procedures and portions). Generally, various kinds of tip electrodes can be attached to a pen-shaped holder with output switches for coagulation and incision. For medical fields including orthopedics, neurosurgery and otolaryngology, “forceps type electrodes” are used, while for endoscopic surgery, exclusive electrodes are introduced.
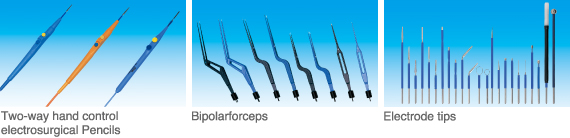
MERA has marketed high-frequency electrosurgical units using the spark gap method that was the previous version for a long time. As for the transistor type electrosurgical unit used in recent years, we have developed many new products over approximately 40 years. Consequently, our products are used in many clinical sites including national/government hospitals, university hospitals, and practitioners.
In addition, receiving opinions or demands from clinical professionals such as physicians, clinical engineers and nurses, we have produced new products introducing new technologies. In recent years, the company has developed a unique complete-concomitant-use model, the “Double type electrosurgical unit,” which features two functions of the electrosurgical generator embedded on one unit. We have already marketed the product addressing procedures in heart surgery, esophageal surgery and orthopedics, including procedures where two operators must concomitantly use two electrosurgical generators. Furthermore, we have actively studied and developed various accessories used in the electrosurgical units. Concerning the development of the patient return electrode, Sekisui Plastics Co., Ltd. and the company have jointly developed new products. The patient skin-friendly “SAS Pad Matrix” and “NE Gel Pad” patient return electrodes for adults and children have been marketed in Japan.
If a patient undergoes surgery in a hospital, his or her body is damaged by the scalpel and needle. As a result, the patient can feel pain and move unconsciously during surgery, and the surgeon can no longer continue. To prevent such a situation, “anesthesia” is applied. Anesthesia makes the patient feel no pain. There are many procedures in anesthesia depending on the administration route to the patient. One such procedures includes inhalational anesthesia. In inhalational anesthesia, the anesthesia is applied by having the patient inhale oxygen, nitrous oxide and volatile anesthetic as a gas. The equipment operating safely and administering these gases is called an “inhalation anesthesia system (whole body anesthesia device).” The system offers the advantage of taking anesthesia to remove pain. In contrast, it has the disadvantage of restraining functions in various parts of the body. To make up for the restrained body functions and monitor the situation, a respirator and monitoring devices for vital signs are used for safer surgery.

 Unlike original breathing in the living body, an anesthesia machine sends air into the patient’s lungs during surgery. In addition, the machine has functions to control rhythm, pressure and volume of inspired air (inhalation) and to adjust the dosage of volatile anesthetic in the inspired gas. We manufactured the first-domestically developed closed circuit-type anesthesia system. Our latest anesthesia system “PIXYS” can finely and precisely control the related parameters to support the advanced medical care that is required in clinical settings.
Unlike original breathing in the living body, an anesthesia machine sends air into the patient’s lungs during surgery. In addition, the machine has functions to control rhythm, pressure and volume of inspired air (inhalation) and to adjust the dosage of volatile anesthetic in the inspired gas. We manufactured the first-domestically developed closed circuit-type anesthesia system. Our latest anesthesia system “PIXYS” can finely and precisely control the related parameters to support the advanced medical care that is required in clinical settings.
 A breathing circuit consists of tubes that connect the anesthesia system and the patient’s mouth. The circuit leads inhaled air from the unit to the patient and leads exhaled air from the patient to the unit. We have marketed a disposable coaxial breathing circuit, “F Breathing Circuit,” for the first time anywhere in the world.
A breathing circuit consists of tubes that connect the anesthesia system and the patient’s mouth. The circuit leads inhaled air from the unit to the patient and leads exhaled air from the patient to the unit. We have marketed a disposable coaxial breathing circuit, “F Breathing Circuit,” for the first time anywhere in the world.
 A tube is used in patients who need a long-term respiratory care and who have a hazard disturbing breathing in the pharynx/larynx. It is designed for airway management. Most tubes used have a soft balloon called a cuff. The “Sofit” and “Sofit clear” made by the company have been developed and designed with great importance placed on safety and operability.
A tube is used in patients who need a long-term respiratory care and who have a hazard disturbing breathing in the pharynx/larynx. It is designed for airway management. Most tubes used have a soft balloon called a cuff. The “Sofit” and “Sofit clear” made by the company have been developed and designed with great importance placed on safety and operability.
 This system is intended to be used for supplying humidified O2 to patients who need oxygen inhalation. The world’s first soft bag for O2 supply is an environmentally-friendly type product, which can reduce CO2 emissions and garbage volume.
This system is intended to be used for supplying humidified O2 to patients who need oxygen inhalation. The world’s first soft bag for O2 supply is an environmentally-friendly type product, which can reduce CO2 emissions and garbage volume.
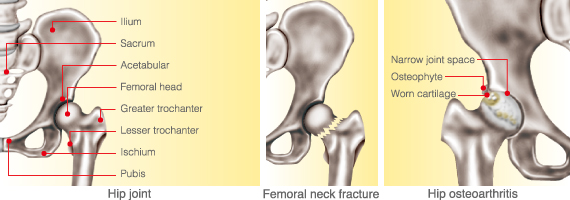
The purposes of total hip replacement are to “relieve pain” and to “recover the joint function.” The hip joint is the biggest joint in the body that supports weight. If it is difficult to alleviate the symptoms of the joint due to disease or injury, various problems arise. For instance, pain on moving, difficulty to use stairs, inability to wear socks or trim nails, and even pain when just standing as the worst case. For patients whose hip joints have been aggravated due to surgery, changing to a prosthesis is expected to reduce the joint pain and recover its function.
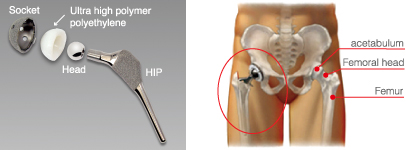
The artificial joint is comprised of four parts as follows:
Head: Plays a role as the femur head
Stem: Implanted into the femur to support stress to the hip joint
Acetabular shell: Plays a role as the articular surface on the acetabular side
Socket: Implanted on the acetabular to support the acetabular shell
The purposes of total knee replacement are to “relieve pain” and to “recover the joint function.” The knee joint is comprised of the thigh, tibia and patella. The cartilage and meniscus on the knee joint have worn for a long period. As a result, pain and transformation, functional disorder (degenerative gonarthrosis) may occur. Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by accumulating synovial fluid or inflammation of the tissue surrounding the joint, resulting in pain and swelling. For patients whose knee joints have been aggravated due to surgery, changing to a prosthesis is expected to reduce the joint pain and recover its function.
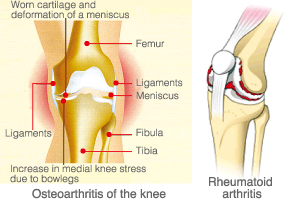
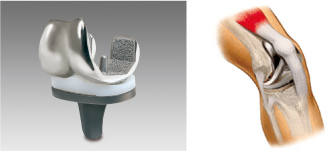
The artificial joint is comprised of four parts as follows:
Femoral component: Plays a role as the joint surface of the femur
Tibial insert: Plays roles as the meniscal and the cartilage of the knee joint.
Tibial component: Implanted on the tibia as a base to support the tibial insert.
Patellar component: Plays a role as the joint surface of the patella
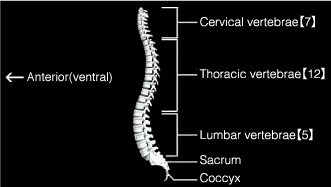
The spine consists of unique-shaped vertebra. Under the cranial bone, there are cervical vertebrae (7), thoracic vertebrae (12) and lumbar vertebrae (5) in tune. Under these vertebrae, there are the sacrum and the coccyx in sequence, which support the body and protect the spine.
If degeneration, transformation, bone fracture or tumor occurs on the spine, the nerves such as the spinal cord and nerve root may be compressed. As a result, symptoms such as pain or numbness may occur. In case that pain, numbness or paralysis is not improved by conservative treatment, spine surgery will be performed. The basic purposes of spine surgery include “removing compression,” which means releasing pressure on the nerve, “fixation,” which means the stabilization of the unstable spine and “correction,” which means the repair of displacement and bending. Such fixation and correction can be performed by using spinal implants consisting of metal screws or rods.